First Digital Adult Reading Test Available on RuStore
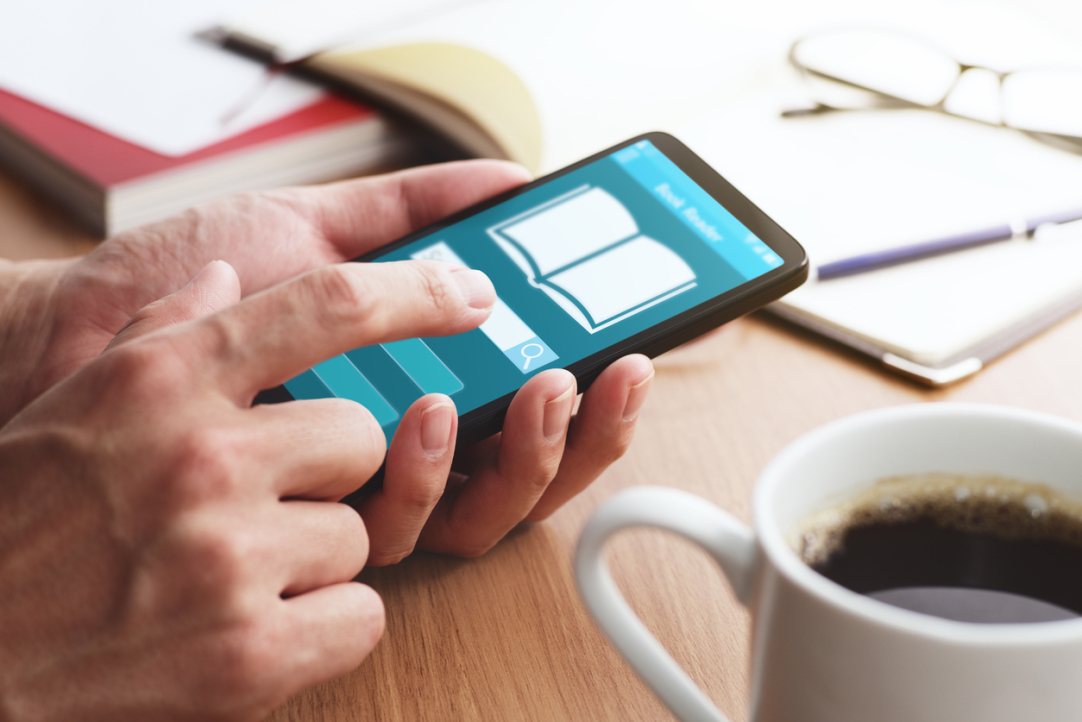

HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain has developed the first standardised tool for assessing Russian reading skills in adults—the LexiMetr-A test. The test is now available digitally on the RuStore platform. This application allows for a quick and effective diagnosis of reading disorders, including dyslexia, in people aged 18 and older.
Reading skills are essential for a social and professional life. For millions of adults with reading impairments, the lack of a timely diagnosis can mean inaccessibility to quality education, career opportunities, and social support. However, for adults in Russia, there was no reliable tool or standard for objectively measuring reading proficiency or comparing results with normative data. The LexiMetr-A digital test fills this gap, offering professionals and researchers an effective way to assess the speed and accuracy of reading, as well as the level of reading comprehension.

Svetlana Dorofeeva
‘The development of LexiMetr-A was a logical consequence of our efforts to create linguistics-based tests for diagnosing speech and reading disorders in children. Adults with reading impairments also need age-appropriate tools,’ says Svetlana Dorofeeva, one of test developers and researcher at HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain.
The test has two parallel versions, one for initial diagnostics and the other for retesting or for assessing the effectiveness of interventions. The versions are balanced in terms of a number of psycholinguistic parameters, such as the length of words in syllables and in letters, the frequency of words, and the complexity of syntactic structures. Each text comes with a set of reading comprehension questions. After reading and marking errors, the application automatically calculates reading parameters and provides information about which syntactic structures were the most difficult. This level of detail is particularly useful for planning remedial work.
The application is aimed at specialists: speech therapists, neuropsychologists, and neurologists working in clinics, educational and research institutions. It includes age-appropriate cutoff levels for different user groups from 18 to 60+ years old, which ensures high diagnostic accuracy. The app replaces paper protocols, manual error counting, and voice recorders. All stages of the test—from text demonstration to error analysis—take place in a digital interface. The results, including audio recordings and markings, are uploaded in a useful format, making it easier to observe and draw conclusions.
The tool will enable informed decisions for selecting a future approach to working with reading difficulties or supporting adults with dyslexia. For instance, a confirmed dyslexia diagnosis could be taken into account by universities when determining a specific assessment system for students with such difficulties.
The developers emphasise that the test will be useful in both clinical and scientific application. The new tool collects an array of audio data and reading indicators, making it a valuable research tool for cognitive linguistics, psycholinguistics, and neuropsychology.

Olga Dragoy
‘Our goal is to make reading diagnostics more accessible and up-to-date. LexiMetr-A is not just a test; it is a practical tool that saves time, provides accurate results, and opens up new possibilities for helping people with dyslexia,’ comments Olga Dragoy, Director of the Centre for Language and Brain, HSE University.
See also:
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Tops Ranking of Universities Participating in Priority 2030 Programme
The Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education has published an updated list of participants in the Priority 2030 programme. A total of 106 universities will receive support this year. HSE University was included in the first group and topped the ranking.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
HSE Scientists Optimise Training of Generative Flow Networks
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have optimised the training method for generative flow neural networks to handle unstructured tasks, which could make the search for new drugs more efficient. The results of their work were presented at ICLR 2025, one of the world’s leading conferences on machine learning. The paper is available at Arxiv.org.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.